Guide entry section:
Guide Entry Text:
It's not always obvious why play stops in soccer.
Often, it is because the referee called a foul. When a foul occurs, possession changes to the team who was fouled and they kick a free kick or penalty kick.
The Essentials of Fouls and Free Kicks (0:31):
Image:
poster image:

Guide Entry Text:
There are two different kinds of free kicks, direct and indirect, and they each have specific rules.
The key difference between the two involves scoring:
- If a player is taking a direct kick and is close to the goal, the player may score without any other player touching the ball. A penalty kick is a type of direct kick.
- If a player is taking an indirect kick, the player cannot score unless another player touches the ball first.
In general, direct kicks are awarded for more serious fouls (dangerous play) and indirect kicks for lesser fouls and other minor issues.
Guide Entry Text:
To Review:
- Fouls are one of the few reasons the action stops in soccer.
- A foul often involves unnecessary or reckless player-on-player contact.
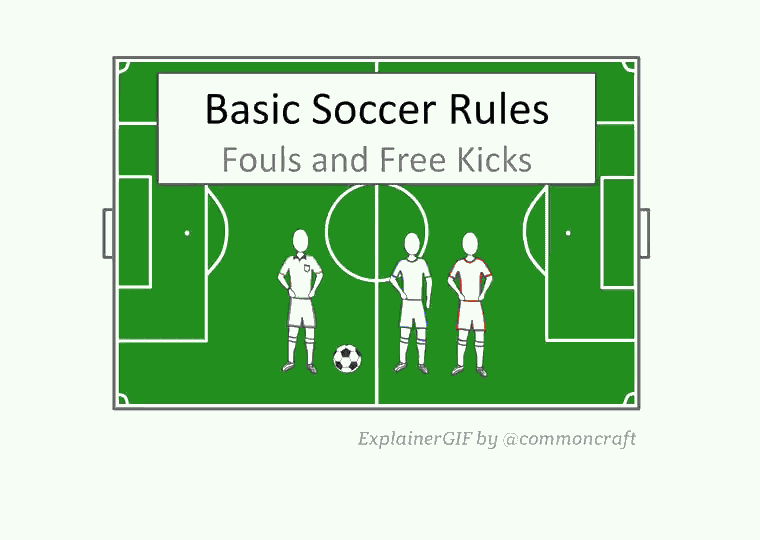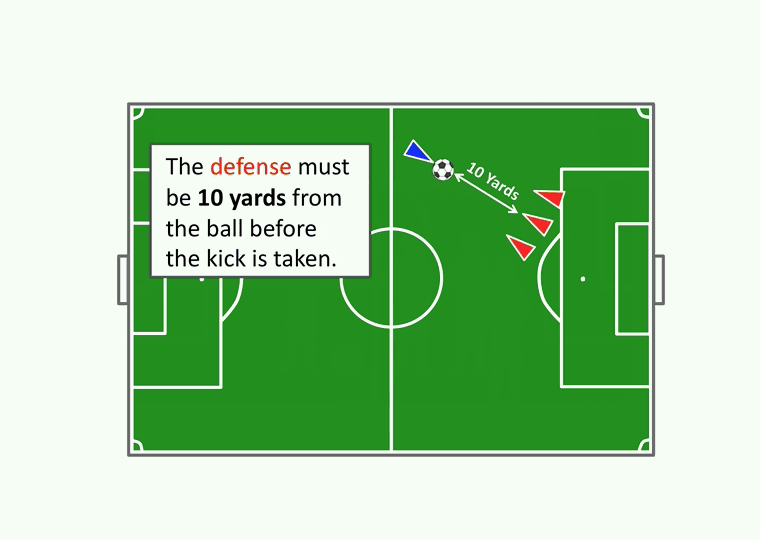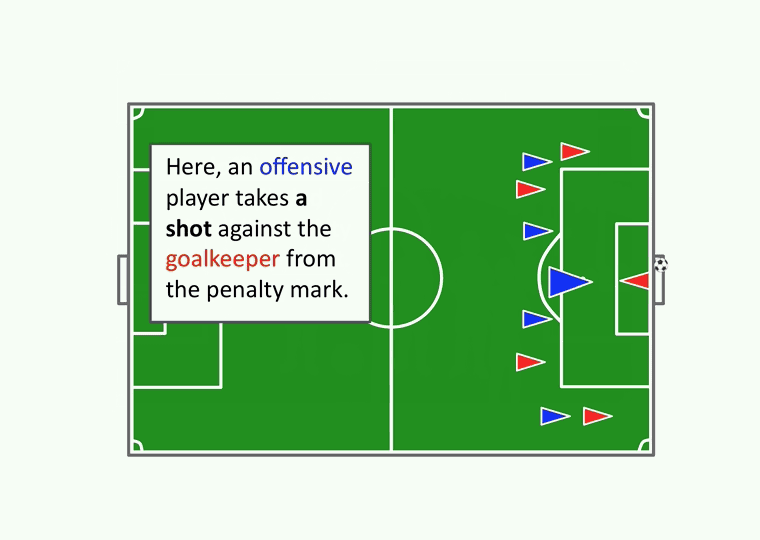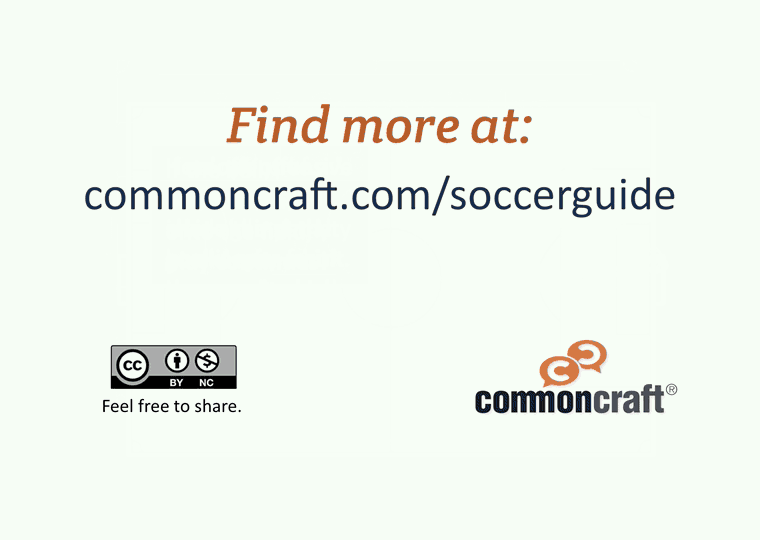
- Fouls result in free kicks with the opposing team at least 10 yards from the ball.
- When a foul is called in the penalty area, it results in a penalty kick.
- Free kicks can be direct or indirect.
