Guide entry section:
Guide Entry Text:
The experience of watching soccer can be perplexing (and frustrating).
Play sometimes stops for no apparent reason. Even the biggest fans are sometimes confused about why a referee called a foul. It's part of the game. But with a little knowledge, you'll start to recognize fouls and you might even disagree - and that's OK.
Part of the allure of soccer is how it is officiated. Like many other sports, many calls are based on the referee's judgment and quick decision making.
At heart, the game is based on 17 laws known at "The Laws of the Game".
17 Laws of the Game
The Laws of the Game are governed by a global organization called FIFA (Fédération Internationale de Football Association) or in English (International Federation of Association Football). FIFA is at the center of global soccer and organizes the World Cup among many other events. FIFA manages the Laws and certifies the referees.
Download a full version of the Laws here.
Here are the laws:
Law 1: The Field of Play
Law 2: The Ball
Law 3: The Number of Players
Law 4: The Players' Equipment
Law 5: The Referee
Law 6: The Assistant Referees
Law 7: The Duration of the Match
Law 8: The start and restart of play
Law 9: Ball in and out of play
Law 10: The Method of Scoring
Law 11: Offside
Law 12: Fouls and Misconduct
Law 13: Free kicks (direct and indirect)
Law 14: The Penalty Kick
Law 15: The Throw-in
Law 16: The Goal Kick
Law 17: Corner kick
Within each of the laws are "interpretations" that become very specific.
The Referees
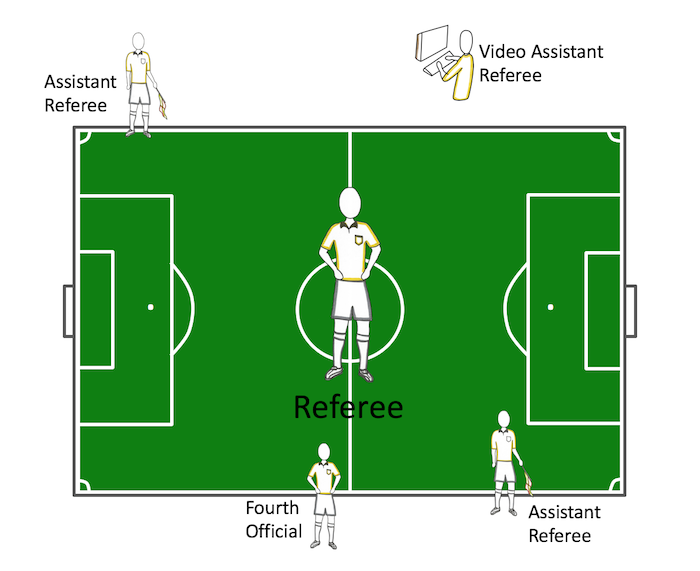
In most high level matches like the World Cup, there are multiple referees - a referee, two assistant referees, a fourth official and a team of video assistant referees.
The duties of each include:
Referee
- Enforces laws of the game (issues penalties)
- Controls the match with other referees
- Official timekeeper of the match
- Ensures ball and equipment are appropriate
Assistant Referee
- Indicates when ball goes out-of-bounds
- Indicates possession when ball goes out-of-bounds
- Indicates offside
- Substitution support
- Aids referee in calls when the referee's view is obstructed
Fouth Official (off-field, not required)
- Administrative duties
- Substitution support
- Visuals (lit signs) for substitutions and stoppage time
Video Assistant Referees or "VAR" (4 referees in an off-field booth with video monitors)
- First use in World Cup
- Uses video footage to make calls
- On field referee can communicate with VAR referee and request video review
- VAR can only be used to make calls regarding goals, penalty decisions, red cards and cases of mistaken identity.
Overall, the Referee manages the whole field and is the bottom line on all calls. Assistant Referees manage the sidelines and raise flags when the ball goes out-of-bounds or a player is offside.
The Referees:
Image:
Guide Entry Text:
To Review:
- The referee enforces and interprets the 17 Laws of the Game.
- The Laws and referees are governed by FIFA, the organization that organizes the World Cup.
- In high profile matches there are often 4 referees: a referee, two assitant referees and a fouth official.
- Each referee has a specific set of duties during the match.
